What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? Introducing Time 4 Whey Protein Professional
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder?
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder – Introducing Time 4 Whey Protein Professional
Here at Time 4 Nutrition, we take an evidence-based approach to the development of all of our products. We make no outlandish claims but just state the findings of published studies which have investigated the efficacy of the ingredients we use. Therefore, you can be secure in the knowledge that everything we recommend is supported by evidence. We also understand that science changes. Consequently, we change our formulations and develop new products in accordance with advances in understanding to keep you at the cutting edge. So, we are proud to announce the launch of Time 4 Whey Protein Professional, the first in a new generation of Time 4 Nutrition products.
You may be familiar with whey protein, as it is one of the most popular and biggest selling supplements on the market today. This is due to the numerous scientific studies that demonstrate the range of great benefits it provides for both health and performance. These include increasing muscle mass (1,12,15,16,) reducing body fat (1, 2, 4) helping to maintain muscle mass during weight loss (4), supressing appetite to aid fat loss, increasing metabolism (2), improving immune function, reducing blood pressure (5), reducing unhealthy blood fats (7), improving blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetics, and increasing the production of glutathione, the body’s master antioxidant (8). It also confers benefits against a wide range of metabolic diseases such as cardiovascular complications, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, cancer and phenylketonuria (17).
However, while it may say whey on the label, not all whey proteins are created equal; the quality and effectiveness of the product can vary greatly between brands. It is not just a matter of how much protein you get per gram of product. There are various types of whey protein, which differ slightly in the processing they have undergone, their composition and the benefits they provide. There also other forms of protein and other substances that science shows work synergistically with whey to provide a superior product and so provide superior results.
In this article, we are going to review some of that research and explain how there’s a lot more to Time 4 Whey Protein Professional than the name suggests.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What’s in Time 4 Whey Protein Professional?
Time 4 Whey Protein Professional is a specially formulated combination of our grass fed peptide protein blend comprising Native (Undenatured) Whey Protein Concentrate, Partially Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate, Micellar Casein, Fermented Amino Acid Blend: LeuSyn®: (Glycyl-L-leucine), L-leucine, Taurine, Lactoferrin, and DigestiZym®.
As we look at each of these ingredients in-depth, you’ll begin to see why Time 4 Whey Protein Professional is such a great product and how it may benefit your health and performance.

What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – Understanding Whey Protein
Before we look in detail at Time 4 Whey Protein Professional, it is important to understand what whey protein is and where it comes from.
Whey protein is a complete, high-quality, easily digested protein. It is the protein fraction of whey, the liquid portion of milk that separates from the curds during the cheese making process. It comprises 20% of total milk protein and is rich in branch chain amino acids and essential amino acids, functional peptides, antioxidants and immunoglobulins (17).
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – How Does Whey Compare to Other Protein Sources?
The results of a study by Devries and Philips (18) showed that whey protein is one of the highest-quality proteins, given its amino acid content (i.e. high in essential amino acids, branch chain amino acids, and leucine) and rapid digestibility. The authors further suggest that whey protein has the ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis to a greater degree than other proteins.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – Time 4 Whey Protein Professional Blend
Time 4 Whey Protein Professional contains a blend of grass fed native (Undenatured) whey protein concentrate and partially hydrolysed whey protein isolate.
These terms may seem a little complicated and confusing but once you understand their meaning, it soon becomes clear how these forms of whey protein can benefit you.

What are the Benefits of Grass Fed Dairy Protein?
You may be thinking does the diet consumed by cows really affect the benefits provided by whey protein? The short answer is yes.
As the term suggests, grass fed cows spend the majority of their time outside grazing on fresh, growing pasture, consuming grass as their main source of food. In winter time, when there isn’t outside pasture available, grass-fed cows are fed hay and other dried leafy forage materials. They do not consume grains or grain by-products. This diet can lead to a healthier animal and different milk composition compared to regular dairy products. In comparison, conventional cows are typically grain-fed.
Although the amount of carbohydrate, protein, and calcium are identical in grass fed and conventional milk, pasture feeding has been demonstrated to have a positive impact on the nutrient profile of milk, increasing the content of some beneficial nutrients such as Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which have important implications for health (19).
Western diets are high in omega-6s and low in omega-3s. A high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio raises the risk of inflammation, heart disease, diabetes, and weight gain. Omega-3 fatty acids, on the other hand, have potent anti-inflammatory effects. They support brain and heart health and have been shown to reduce symptoms of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of risk factors that increase the chances of developing heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. They are responsible for numerous cellular functions, including signalling, cell membrane fluidity, and structural maintenance and regulation of the nervous system, blood pressure, blood clotting, glucose tolerance, and inflammatory processes (19).
According to a review by Gammone and colleagues (20), the consumption of omega-3s may also support the immune system and enhance exercise performance. For example, athletes who consumed omega-3s improved their recovery time, reduced their chances of illness, and had superior performances in competition. In addition, the consumption of omega-3s enhanced mood.

What is Conjugated Linoleic Acid?
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) is a group of fatty acids found in a limited number of foods. The highest levels of CLA occur in ruminant animals, with beef, milk-fat, and cheese, being the most common animal sources. Technically speaking, CLA is a type of polyunsaturated, or naturally occurring trans fat, but unlike artificial trans fats, which can be harmful when consumed in high amounts, CLA is believed to provide a variety of potential health benefits and perform a range of important physiological functions. These range from reducing body fat and increasing muscle to reducing inflammation and enhancing immunity. While the human body is capable of producing the majority of fatty acids it requires, it cannot produce linoleic acid, hence it is referred to as an essential fatty acid. Therefore, we must consume it in our diet. To learn more about CLA, just click the link below.
The benefits of grass fed don’t end there.
When cattle are grass-fed, health-promoting substances that occur in plants referred to as phytonutrients, are found in their meat and milk in amounts comparable to those present in plant foods. These may have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and cardiovascular health supporting properties (21).
What is Native (Undenatured) Whey Protein?
Two terms that are increasingly associated with whey protein are ‘undenatured’ and ‘native’. Essentially, they mean the same thing, and refer to the type of processing whey has undergone.
Native, or undenatured, whey protein is produced by the filtration of unprocessed raw milk at low temperature with the sole purpose of making whey protein supplements. This allows it to maintain all of its amino acids intact and gives native whey higher levels of the amino acid leucine, a powerful driver of muscle growth. More common, cheaper whey concentrates are the by-product of cheese making that employs high temperature processing methods. These involve separating out the whey, leaving it to dry at high temperatures before it is used to produce a whey supplement.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Undenatured Whey Protein?
The results of a randomised control by Hamarsland et al., (22), which compared the effects of a native whey supplement with a regular whey product and milk, showed that native whey increased blood leucine concentrations to a greater degree than regular whey and milk. Native whey also produced a greater phosphorylation of p70S6K, which induces protein synthesis, than milk 180 minutes after exercise. In addition, muscle protein synthesis rates increased 1-3 hours after exercise with regular whey and 1-5 hours after exercise with native whey.
What are Bioactive Peptides and Immunoglobulins?
Whey protein is also rich in the bioactive compounds and growth factors, which provide many health benefits, but must remain in their undenatured form to exert these properties.
Two such substances are bioactive peptides and immunoglobulins.
Bioactive peptides (BP) are formed by amino acids joined by peptide bonds and are derived from a number of proteins found in whey. These include beta-lactoglobulin (beta-Lg), α-Lactalbumin (α-La), bovine serum albumin and lactoferrin.
They play a significant role in human health, particularly the digestive, endocrine, cardiovascular, immune, and nervous systems. In addition, they have immunomodulatory, antibacterial, anti-hypertensive, antioxidative and opioid-like properties, and help to decrease cholesterol levels.

What are Immunoglobulins?
Undenatured grass-fed whey is rich in immunoglobulins. These are a class of proteins which occur naturally in whey, and function as antibodies, helping to fight infection. They bind to bacteria, toxins and other harmful molecules and remove them safely from the body. In undenatured whey, they are preserved intact so that their integrity is not compromised.
A number of different immunoglobulins occur in whey, which play specific roles in immunity:
- IgM can be thought of as being the first line of immune system defence.
- IgG This is the most common type of human antibody and makes up about 75-80% of the antibody population.
- IgA inhibits bacterial and viral adhesion to epithelial cells, which line the surfaces of organs in the body and function as a protective barrier.
To learn more about the many benefits bioactive peptides and immunoglobulins in Time 4 Whey Protein Professional can provide, just click the link below.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Whey Derived Immunoglobulins and Immunity?
The results of a study by Ha et al., (48) showed that supplementation with whey protein increased the levels of specialised immune cells known as B cells and T cells in response to an antigen. The authors concluded that whey protein may activate adaptive immunity (IgG) against an antigen by modulating T cells.

What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – Whey Protein Isolate Versus Whey Protein Concentrate
Time 4 Whey Protein Professional contains a blend of two forms of whey. These are whey protein concentrate and partially hydrolysed whey protein isolate.
While both whey isolate and concentrate are great sources of complete protein, providing you with all of the amino acids you need to build and maintain a lean, muscular physique, and both increase the release of anabolic hormones, they are slightly different. Therefore, each can provide particular benefits.
Whey concentrate and isolate undergo several processing steps to increase their protein content. After a sufficient protein concentration is achieved, the liquid can be dried to form whey concentrate powder. This comprises up to 80% protein by weight and is typically low in fat and cholesterol and contains bioactive compounds as well as growth factors and small amounts of carbohydrates in the form of lactose. It is also rich in both branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and glutamine. In comparison to other protein sources, such as meat, whey concentrate is quickly absorbed by the body, although not as quickly as whey isolate.
Whey isolate goes through a more intense processing phase than whey concentrate. This removes virtually all of the carbohydrates and fat yielding highly pure protein content of 90% or more by weight. It is also more quickly absorbed by the body than whey protein concentrate.
Although the processing steps used in the production of whey isolate result in a higher protein content, they also result in a reduction in some bioactive compounds and growth factors and lower levels of carbohydrates, lactose and fat than whey concentrate. Therefore, combining both whey isolate and concentrate provides you with benefits of each.
What is Partially Hydrolysed Whey Protein Isolate?
The form of whey protein isolate in Time 4 Whey Professional is partially hydrolysed. This means that the whey has undergone a process known as enzymatic hydrolysis to break the protein into smaller protein fragments using enzymes similar to those produced in the human digestive system.
Protein molecules can be either ‘partially’ hydrolysed, meaning their amino acid chains are broken down into smaller segments. Alternatively, they can be fully hydrolysed, meaning each amino acid has been isolated.
Hydrolysed whey has the same amino acid content as non-hydrolysed, but as the protein fragments in the hydrolysed versions are smaller, they are more rapidly digested. This allows the amino acids to enter your muscles more quickly to enhance growth.
As hydrolysed proteins are essentially pre-digested, the body can not only absorb them more quickly than intact proteins, but also more easily and they are better tolerated by the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This is particularly important for people with digestive disorders and food allergies or sensitivities.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Hydrolysed Whey Protein?
Shin and colleagues (23) investigated the effects of hydrolysed whey protein on muscle atrophy caused by immobilisation. The results showed that hydrolysed whey protein attenuated muscle atrophy by enhancing the net protein content, regulating muscle protein synthesis and degradation. This resulted in increases in grip strength, muscle weight, and cross-sectional area of muscle fibres.
The authors noted whey protein hydrolysates have the best nutrient quality among food proteins and are a necessary and probable candidate for developing functional food to prevent muscle atrophy.

What is Micellar Casein Protein?
In addition to whey protein concentrate and isolate, Time 4 Whey Protein Professional also contains micellar casein protein.
While whey comprises of 20% milk protein, casein accounts for the remaining 80%. One litre of milk contains 32 grams of protein (26g casein and 6g whey). Like whey protein, casein is a complete protein which provides all of the essential amino acids the body needs for growth and repair (24). Also, like whey, there are different types of casein, the nutritional value of which is influenced by the type of processing they have undergone.
The two main forms are casein hydrolysate, which is pre-digested and rapidly absorbed, and micellar casein. Time 4 Whey Protein Professional contains micellar casein protein. Like our whey protein, this is low temperature undenatured, allowing it to maintain all of its amino acids, bioactive compounds and growth factors in their most powerful natural state.
Micellar casein concentration is accomplished by the use of a process known as ultrafiltration or microfiltration. Under high pressure, but at a low temperature, milk is forced through an extremely fine filtration screen that traps the casein and most of the whey protein molecules, but without eliminating the natural minerals found in milk, such as calcium, magnesium, and others.
This a non-denaturing mechanical process, which allows the micellar casein to maintain its natural globular structure and comprises particles known collectively called as micelles.
Casein micelles are composed of four main types of proteins: αS1‐casein, αS2‐casein, β‐casein, and k‐casein, which influence various bodily functions including digestion and immunity.
These different casein proteins possess different functional properties due to their primary amino acid sequence. For example, αS1‐casein plays an important role in the capacity of milk to transport calcium phosphate and also has antioxidant properties. While k‐casein is responsible for an increased efficiency of digestion and the inhibition of gastric pathogens.
Additionally, as micellar casein has not been acid treated in production, is it more effective at forming a ‘bolus’ (a small rounded mass of chewed food) in the stomach, which helps to enhance its time release qualities.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – Casein Protein Versus Whey Protein
Although casein and whey are both derived from milk and offer similar benefits, they differ in a number of ways and complement each other.
While whey contains more of the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) leucine, isoleucine and valine, casein contains a higher portion of the amino acids histidine, methionine and phenylalanine. It also provides two essential elements, calcium and phosphorus.
Casein and whey protein contain different bioactive compounds that benefit your health in a multitude of ways. Casein contains several bioactive peptides that have been shown to benefit the immune, cardiovascular and digestive systems. For example, casein-derived peptides have been shown to lower blood pressure and reduce the formation of blood clots.
Glycomacropeptide (GMP) a peptide derived from kappa casein, exhibits antibacterial and antithrombotic activities (25).
Alpha lactalbumin (LA) demonstrates antiviral, antitumor and anti-stress properties while lysozyme is effective in treatment of periodontitis and prevention of tooth decay (25).
In contrast to whey protein’s rapid digestion, micellar casein protein is referred to as a ‘time-release’ protein because it is digested slowly, supplying your muscles with amino acids at a low level over a period of up to 8 hours after consumption to ensure optimum growth and recovery (26, 27). This also helps you to feel full longer, which is particularly useful when you are trying to get leaner, and makes it ideal for consumption before fasting situations, such as sleep. It can also help to reduce post-exercise soreness and prevent cravings during the night and extreme hunger first thing in the morning.
Therefore, athletes often consume casein before bed when it can reduce muscle breakdown as they fast overnight. In short, this means that your muscle cells are able to synthesize protein during times when your body might normally be breaking down its own muscle tissue. Consequently, this ability of micellar casein protein has led to it being referred as ‘anti-catabolic’.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Consuming Casein Protein Before Bed?
A study by Snijders and colleagues (28) assessed the impact of casein protein supplementation before sleep on muscle mass and strength gains during a resistance training programme. The results of the study showed that those subjects consuming a casein protein supplement before bed increased type 2 muscle fibre size by 8.4cm2 compared to 4.8cm2 in the placebo group. The study also found that the casein group achieved significantly greater gains in strength (20%) in comparison to the placebo group.
In light of evidence such as this, the International Institute of Sports Nutritionists now recommend a pre-sleep intake of casein protein to increase overnight muscle protein synthesis (29).
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – Casein is Not Just a Bedtime Drink
It is important to note that micellar casein protein isn’t just for consumption at night; with its slow release of critical nutrients, it is ideal for consumption at breakfast, bedtime and any situation that involves short-term fasting.
For example, it is recommended that we consume high quality protein every 3-4 hours across the day to maximise muscle protein synthesis (30); however, this is often difficult due to the demands of modern living. You may have your breakfast at 6am and then be unable to consume the requisite amount of protein until 12 pm. This is a full six hours of fasting. In these situations, micellar casein protein can provide you with that gradual supply of essential amino acids and other important nutrients.

What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – How Effective is Micellar Casein Protein for Building Muscle?
Numerous studies have shown that micellar casein protein is very effective for promoting muscle growth and strength, because, like whey protein, it provides all of the essential amino acids needed for muscle protein synthesis (12, 13, 14).
For example, a study by Tipton and colleagues (12) examined the acute response of muscle protein balance in response to the consumption of casein and whey protein after resistance exercise.
Volunteers were randomly assigned to one of three groups. Each group consumed one of three drinks: placebo, 20g of casein or whey protein 1 hour after a resistance training session. The results of the study showed that consuming both whey protein and casein after exercise resulted in similar increases in muscle protein synthesis.
In addition, casein protein provides a powerful anti-catabolic effect, as it enhances long-term muscle mass by reducing protein breakdown (10, 11). This process occurs on a daily basis when your body is low on energy and amino acids, and is accelerated during exercise or when reducing bodyfat levels, such as during contest prep.
To learn more about the specific benefits of micellar casein protein, just click the link below.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Combining Whey Protein and Casein Protein?
We have seen that both whey and casein protein can provide numerous benefits, but is there any additional benefit to be gained from combining them?
Firstly, it is important to remember that it is natural for us to eat a combination of whey and casein proteins, as they occur together in dairy foods, and therefore, can work together to provide a steady influx of amino acids for muscle growth and repair, but what does the science say?
Boirie and colleagues (10) tested the hypothesis that the speed of absorption of dietary amino acids by the gut varies according to the type of ingested dietary protein, which can affect post-feeding protein synthesis, breakdown, and deposition. A group of healthy adults consume a casein and whey protein supplement in a single meal. The results showed that whey protein induced a dramatic but short increase of plasma amino acids, while casein induced a moderate increase with a prolonged plateau. Whole body protein breakdown was inhibited by 34% after casein ingestion but not after whey protein ingestion. Postprandial protein synthesis was stimulated by 68% with the whey protein meal and to a lesser extent (+31%) with the casein.
The authors concluded that the speed of protein digestion and amino acid absorption from the gut has a major effect on whole body protein anabolism after a single meal. Therefore, the body’s response to slow and fast proteins has implications for both health and performance.
The bottom line is that a combination of both whey and casein protein provides a better anabolic effect as it delivers a sustained feed of muscle building amino acids into the blood stream to ensure optimum growth and recovery.
The efficacy of a combined whey and casein supplement was further demonstrated by the results of a study by Willoughby et al., (31) A group of men participating in a strength training programme, consumed either a 20g protein supplement (14g whey and casein protein and 6g free amino acids) or a dextrose placebo.
The subjects consuming the whey and casein supplement had greater increases in total body mass, fat-free mass, thigh mass, muscle strength, serum IGF-1, IGF-1, mRNA, MHC I and IIa expression, and myofibrillar protein, all of which are indicators of protein muscle synthesis and anabolism, in comparison to those subjects consuming the dextrose placebo.
Consuming a combination of casein and whey protein has also been shown to help reduce body fat while increasing muscle. The results of a study by Kerksick et al., (32) showed that male resistance trained subjects who took a protein supplement containing whey and casein protein increased lean tissue mass and decreased fat mass to a greater degree, in comparison to subjects who consumed either a carbohydrate placebo or a whey protein plus a branched-chain amino acids supplement.

What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – Absorption and Dose Size
Another factor to consider is the rate of absorption. In their position stand on protein and exercise, the International Society of Sports Nutrition (29) suggest that rapidly digested proteins that contain high proportions of essential amino acids (EAAs) and adequate leucine, are most effective in stimulating muscle protein synthesis.
Therefore, as whey isolate is absorbed faster than whey concentrate, it can access the muscles faster and the regeneration process can begin more quickly.
So, you may be thinking that in order to maximise muscle growth and repair, consuming as much fasting acting protein as possible would be the best approach. However, it is a little more complicated than that.
A study by Bilsborough and Mann (33) showed that the rate at which the gastrointestinal tract can absorb amino acids from dietary proteins is limited to between 1.3 to 10 g/h.
The size of the protein dose is also important, and bigger is not always better.
Symoms and colleagues (34) compared changes in muscle protein synthesis and anabolic efficiency in response to a single 30g and a 90g protein meal. The results of the study showed that ingestion of more than 30g of protein in a single meal does not further enhance the stimulation of muscle protein synthesis. Findings such as these have led the International Society of Sports Nutrition (29) to recommend a protein dose of 20–40 g to maximize muscle protein synthesis. Time 4 Whey Protein Professional provides you with approximately 26g of high quality protein per standard serving when mixed with water.
Although the post-exercise ingestion (immediately to 2 hours after) of high-quality protein source is important, as it stimulates significant increases in muscle protein synthesis, the anabolic effect of exercise is long-lasting (at least 24 hours) (30). Therefore, the body requires a consistent supply of amino acids over an extended period of time. Consequently, it is recommended that protein doses should ideally be evenly distributed, every 3–4 hours (30) across the day to accommodate this demand.
Consuming protein this often can be difficult for many people, due to the constraints of a busy life and work schedule. The difference in absorption rates of the types of whey proteins in Time 4 Whey Protein Professional helps to ensure your body is supplied with a steady stream of vital amino acids to optimise your recovery and adaptation to exercise.
As we have seen, to further enhance this effect, Time 4 Whey Protein Professional also contains the more slowly digested low temperature undenatured micellar casein protein. This has been shown to be particularly effective when taken before bed to increase overnight muscle protein synthesis.

What are the Benefits of Fermented Amino Acids?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. They play an important role in many essential processes in the body, including muscle growth and repair, regulating gene expression, cell signalling, and immunity.
In addition to the amino acids that occur naturally in whey and casein protein, Time 4 Whey Protein Professional also contains a fermented amino acid blend comprising L-leucine, taurine and Glycyl-L-Leucine.
Before we look at the specific benefits provided by these amino acids, it is important to understand the processing that they have undergone.
Amino acids can be produced by a variety of different methods. One of the most common is via a harsh acid-based process that extracts them from animal products, such as duck feathers, fur and even human hair.
The amino acids in Time 4 Whey Protein Professional are produced by fermentation. This is a natural process which involves fermenting plant-based ingredients with microorganisms, like probiotic bacteria. The microorganisms use various carbon sources such as glucose and fructose to produce the amino acids. The process is similar to how other fermented food products are made such as yogurt, beer and vinegar. As no animal products are used, and no harsh chemicals or high temperature processes are involved in production, this results in a more natural, superior quality product that is suitable for vegetarians.
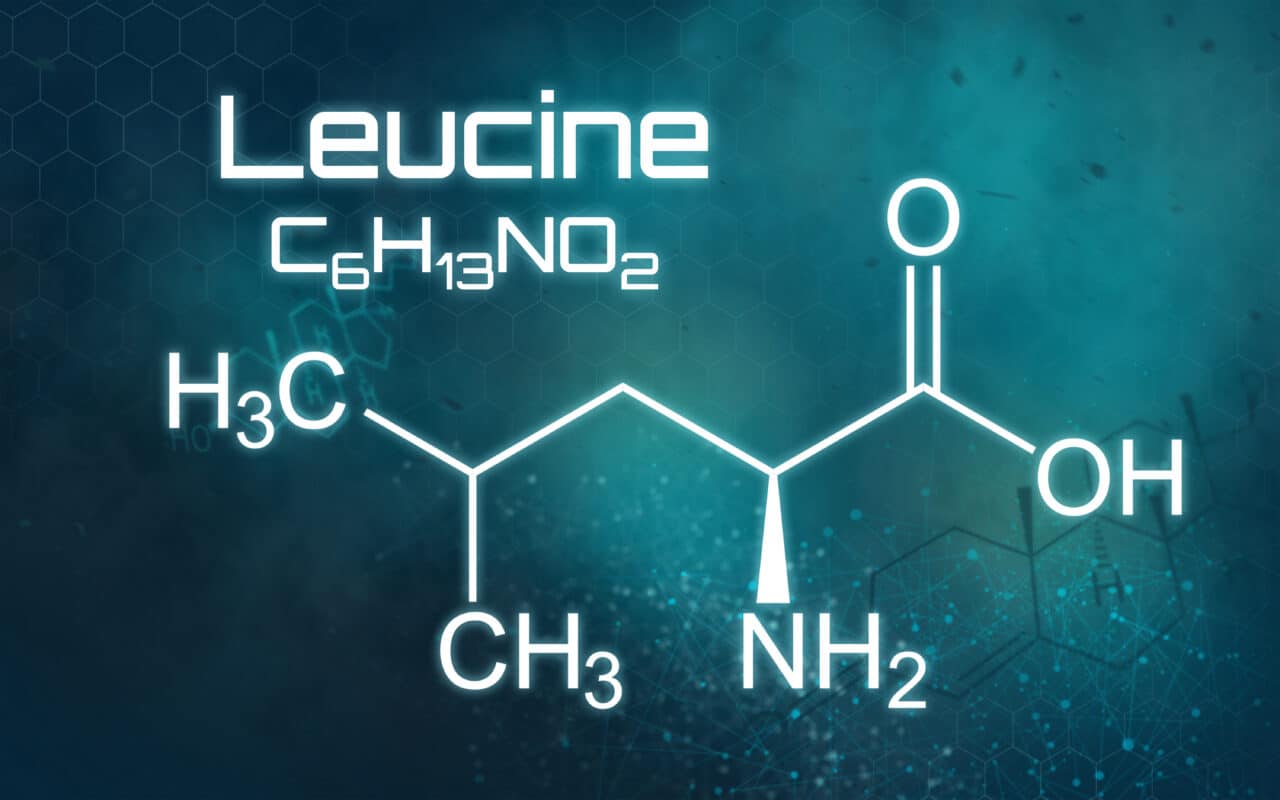
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What is Leucine?
Leucine is an essential amino acid which is important for muscle protein synthesis and many other functions, including the regulation of blood-sugar levels, growth and repair of muscle and bone tissue, growth hormone production, and wound healing. It also prevents the breakdown of muscle proteins after trauma or severe stress and can enhance elements of athletic performance, including strength, endurance and power.
So important is leucine, that the World Health Organization and International Institute of Sport’s Nutrition both issue guidelines regarding how much of this amino acid we should consume.
The World Health Organization states that healthy adults should obtain 18 mg of leucine per pound (39 mg per kg) of body weight per day. This equates to approximately 3.1 grams for a 175-pound (80-kg) person. However, it is important to understand that this is the minimum required to maintain health, not the amount required by individuals wishing to optimise muscle mass.
The International Institute of Sport’s Nutrition’s latest position stand on protein and exercise (29) states that rapidly digested proteins that contain high proportions of essential amino acids (EAAs) and adequate leucine, are most effective in stimulating muscle protein synthesis. The authors suggest that acute protein doses should strive to contain 700-3000 mg of leucine and/or a higher relative leucine content, in addition to a balanced array of the essential amino acids (EAAs). Time 4 Whey Protein Professional provides 3.5 grams of leucine per 30g serving.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Leucine?
A number of studies have demonstrated the benefits provided by leucine supplementation.
Crowe and colleagues (35) investigated the effects of dietary leucine supplementation on the exercise performance of outrigger canoeists. The subjects underwent testing before and after 6-week supplementation with either L-leucine or a placebo. The results showed that leucine supplementation resulted in significant increases in plasma leucine and total BCAA concentrations. Upper body power and work increased in both groups after supplementation but power was significantly greater after leucine supplementation compared to the placebo. In addition, rowing time increased and average RPE decreased with leucine
A review by Mero (36) demonstrates the significant decreases in plasma or serum levels of leucine that occur following exercise and how supplementation can address this. These include aerobic (11 to 33%), anaerobic lactic (5 to 8%) and strength exercise (30%) sessions. One study cited in the review showed that basal fasting serum leucine levels decrease by 20% during 5 weeks of speed and strength training in power-trained athletes on a daily protein intake of 1.26 g/kg bodyweight. However, leucine supplementation of 50 mg/kg bodyweight/day, supplementary to a daily protein intake of 1.26 g/kg bodyweight/day, appeared to prevent the decrease in the serum leucine levels in this group.
Furthermore, BCAA supplementation (76% leucine) in combination with moderate energy restriction has been shown to induce significant and preferential losses of visceral adipose tissue (abdominal fat) and to allow maintenance of a high level of performance.
Although leucine is thought to be important for skeletal muscle growth due to its ability to acutely activate mTORC1 and enhance muscle protein synthesis, little data exist regarding its impact on skeletal muscle size and its ability to produce force. Martin and colleagues (37) assumed a tissue engineering approach in order to test whether supplementing culture medium with leucine could enhance mTORC1 signalling, myotube growth, and muscle function. The results showed that supplementation with leucine caused an increase in muscle tissue size and maximal contractile force capacity.
Bauer and colleagues (38) investigated the effects of a vitamin D and leucine-enriched whey protein on muscle mass and function in older adults. The results of the study showed that the whey protein supplement provided improvements in muscle mass and lower-extremity function among sarcopenic older adults in comparison to the control
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What is Taurine?
Taurine is an amino acid which is highly expressed in various tissues, including skeletal muscle, where it is involved in the ion channel regulation, in the modulation of intracellular calcium concentration, and where it plays an important role as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory factor. It also plays a role in maintaining proper hydration and electrolyte balance; forming bile salts, which play an important role in digestion; regulating minerals such as calcium within the cells; supporting the general function of the central nervous system and eyes; and regulating the immune system. Although it is one of the few amino acids not incorporated into proteins, taurine is one of the most abundant amino acids in the brain, retina, muscle tissue, and organs throughout the body.
Benefits of supplementation include enhancing exercise performance, combating diabetes, improving cardiovascular output, eye and liver health and hearing, and helping to protect the nervous system.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Taurine?
A review by Kurtz et al., (39) investigated the effects of taurine on sports and exercise performance. The results showed improvements in VO2max, time to exhaustion, 3 or 4 km time-trial, anaerobic performance, muscle damage, peak power, and recovery. Taurine also caused a change in metabolites. These include a decrease in lactate, creatine kinase, phosphorus, inflammatory markers, and improved glycolytic/fat oxidation markers.
The authors suggest that taurine supplementation improves aerobic performance, anaerobic performance (strength, power), recovery (DOMS), and a decrease in metabolic markers (creatine kinase, lactate, inorganic phosphate).
Doss et al., (40) investigated the therapeutic effects of taurine in attenuating muscle atrophy, Specifically, the paper investigated taurine’s ability to reduce the expression of two key molecules involved in the atrophy process, atrogin-1 and MuRF-1. The results showed that taurine supplementation had a downregulatory effect on the transcriptional expression profile of both atrogin-1 and MuRF-1. The authors suggest that taurine has the potential to inhibit muscle atrophy and can be developed as a safe treatment option against muscle loss.
Sarcopenia that occurs with advancing age is characterized by a gradual loss of muscle protein due to the activation of catabolic pathways, increased level of inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. An invitro study by Barbiera and colleagues (41) analysed the effect of taurine in the modulation of different signalling pathways known to be dysregulated in sarcopenia. The results showed that the administration of high levels of taurine in myogenic L6 cells stimulates the differentiation process by downregulating the expression of molecules involved in inflammatory pathways and modulating processes such as autophagy, the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components, and apoptosis, programmed cell death. In light of these findings, the authors suggest that taurine supplementation may represent a strategy to delay the loss of mass and functionality in ageing muscles.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What is LeuSyn: (Glycyl-L-leucine)?
Glycyl-L-leucine is our advanced leucine delivery system. Throughout this article we have seen the importance of leucine in driving muscle growth and repair. The inclusion of glycyl-L-leucine helps to enhance the speedy and efficient uptake of leucine into the muscles.
Technically speaking, Glycyl-L-leucine is a dipeptide. This is a compound that occurs when two amino acids are joined together by a peptide bond. The amino acids contained in dipeptides, can still perform their individual roles when broken down by the body but also have particular functions when in their dipeptide form.
In the case of Glycyl-L-leucine, the two amino acids are leucine, which we have already discussed in its free form, and glycine.
Glycine plays an important role in a variety of processes within the body. These include:
- Protein synthesis (constitutes 1/3 of amino acids in collagen and elastin)
- The production of the master oxidant glutathione
- Reducing inflammation
- The formation of creatine
- Improving sleep quality
- Heart health
- Reducing muscle wasting
- Reducing diabetes
- Protecting the liver from alcohol damage
A number of studies have demonstrated the important role glycine plays in leucine absorption. For example, Ham and colleagues (42) found that leucine failed to stimulate muscle protein synthesis in mice suffering with muscle wasting when pre-treated with the amino acid l-alanine. However, when mice were pre-treated with glycine, protein synthesis was stimulated significantly by leucine (+51%).
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Glycyl-L-Leucine?
A study by Cheeseman and Parsons (43) showed that when glycyl-L- leucine is present in the intestines with free amino acids, additional amounts of L-leucine and of glycine are transferred into the vascular system.
An additional benefit of Glycyl-L-leucine may be a reduction in fatigue during exercise. Han and colleagues (44)investigated the anti‑fatigue effects of Danish pig placenta (DPP) and its major dipeptides, including leucine‑glycine (LG) and glycine‑leucine (GL). The results demonstrated that oral treatment of mice with DPP, LG and GL increased the time to exhaustion during treadmill exercise. It also reduced the levels of lactate dehydrogenase, lactate, creatine kinase and blood urea nitrogen, while enhancing muscle and liver glycogen stores and levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is associated with increased performance.

What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What is Lactoferrin?
Lactoferrin is a bioactive peptide found naturally in milk. Its main functions in the body include binding with iron and transporting it, and fighting infection. It has been found to provide antioxidant, anti-inflammatory antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiparasitic and antitumor effects, and helps to protect the lining of the gut.
What is the Best Whey Protein Powder? – What Does the Science Say About Lactoferrin?
A study by Berluttie et al., (45) highlighted lactoferrin’s important role in immune regulation and defence mechanisms against bacteria, fungi and viruses. Lactoferrin’s iron withholding ability is related to inhibition of microbial growth. It also interacts with microbial, viral and cell surfaces thus inhibiting microbial and viral adhesion and entry into host cells.
Lactoferrin, along with lactalbumin, has been associated with improved weight loss and glycaemic control. A study by Zapata and colleagues (46) showed dietary lactalbumin and lactoferrin improved energy balance and metabolism, including glucose clearance, and decreased adiposity.
However, like other milk proteins, in order to gain the maximum benefit provided by lactoferrin the whey protein must be undenatured. Nguyen and colleagues (47) found that that low-heat-treated whey protein had elevated levels of lactoferrin compared with that of standard whey protein.
It also contained higher levels of transforming growth factor-β2. This a form of cytokine, a type of small protein important in cell signalling. It helps to regulate cellular immune responses, cell growth and differentiation, apoptosis, cell movement, the production of new blood vessels and extracellular matrix production (material secreted by cells that fills spaces between the cells in a tissue, protecting them and helping to hold them together).

What are Digestive Enzymes?
To you help to obtain the maximum benefit from all of the great ingredients in Time 4 Whey Protein Professional, we have included Digestizyme®.
Digestive enzymes are substances that help us to digest food. They are released by the salivary glands and cells lining the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine and secreted into the digestive tract, where they help to break down food into its component nutrients. They do this by splitting the large, complex molecules that make up proteins, carbohydrates, and fats into smaller ones This then allows them be absorbed across the gut wall into the bloodstream, where they can travel to where they are needed in the body, such as the muscles.
If this system of enzyme production and use does not work effectively, we will fail to absorb all of the nutrients from the food and supplements we consume, which may have a negative effect on both our health and performance. As we age, our natural production of enzymes declines. This may also occur when we’re unwell or under stress.
Digestizyme® is one of the UK’s strongest enzyme formulas, containing a broad range of plant-sourced enzymes which aid the digestion of proteins, fat and carbohydrate. These enzymes have been carefully selected due to their resistance to degradation in the acidic environment of the stomach, thereby allowing them to reach the small intestine where majority of digestion and absorption occurs.
Digestizyme® blend
| Lipase | Breakdown of fats | Amylase | Digestion of carbohydrates |
| Protease 4.5 | Digestion of proteins in more alkaline conditions | Protease 3.0 | Digestion of proteins in acidic conditions |
| Glucoamylase | Digestion of fats | Cellulase | Helps to digest fibre and plant based foods |
| Bromelain | Digestion of protein | Papain | Digestion of tough protein fibres |
Great Tasting Protein Powders
Here at Time 4 Nutrition, we are known for our great tasting products and our new Whey Protein Professional is no exception. Rather than buy generic off the shelf flavours, we have worked with a top flavour house to develop a fantastic new range to suit all tastes while ensuring that they do not compromise the nutritional value of the product.

In Summary….
Time 4 Whey Protein Professional sets the standard for a new era of evidence-based whey protein supplements. It provides you with the highest quality whey protein concentrate, partially hydrolysed whey isolate and casein protein from grass fed sources in their undenatured form, making them rich in amino acids, bioactive peptides and immunoglobulins. We have also included the fermented amino acids leucine and taurine for enhanced muscle growth and exercise performance, Glycyl-L-leucine to maximise the uptake of leucine, lactoferrin to enhance recovery and immunity, amongst many other benefits, and Digestizyme to aid digestion, thereby ensuring you get the maximum benefit from all of these great ingredients. You can rest assured that Time 4 Whey Protein Professional contains absolutely no cheap fillers, such as skimmed milk powder, and delivers up to 85g of high quality, great tasting protein per 100g. Isn’t it time for you to go pro!

